The main causes of death of victims in road accidents are the following factors:
- injuries incompatible with life - 20%;
- ambulance delay - 10%;
- inaction or incorrect actions of eyewitnesses of the accident - 70%.
The death toll could have been significantly lower if the victims of the accident had been provided with qualified first aid. Unfortunately, the death of a significant number of people occurred not so much because of the severity of the injuries, but because of the wrong actions of those who provided them with first aid, or because of the inaction of others.
In order not to lose precious time, and often human life becomes the price of delay, it is necessary to clearly understand the algorithm of actions in situations related to traffic accidents in which there are victims. If you still have to study at a driving school, pay full attention to the classes on providing medical care. In a critical situation, this knowledge can be very useful.
Failure to provide the necessary assistance entails liability in accordance with the law. Thus, the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation provides for two articles:
Article 124. Failure to provide assistance to a patient
Failure to provide assistance to a patient without good reason by a person who is obliged to provide assistance in accordance with the law or with a special rule, if this negligently entailed the infliction of moderate harm to the health of the patient, is punishable by a fine in the amount of up to forty thousand rubles or in the amount of the wage or other income of the a period of up to three months, or by corrective labor for a term of up to one year, or by arrest for a term of two to four months.
The same act, if it caused by negligence the death of a patient or the infliction of grave harm to his health, shall be punishable by imprisonment for a term of up to three years, with or without deprivation of the right to occupy certain positions or engage in certain activities for a term of up to three years.
Please note that the rules traffic(clause 2.5) oblige the driver to provide first aid to the victims in case of an accident. It is these obligations, regulated by the Rules of the Road, that are discussed in article 124.
Article 125. Leaving in danger
Knowingly leaving without help a person who is in a state of danger to life or health and deprived of the opportunity to take measures for self-preservation due to infancy, old age, illness or due to his helplessness, in cases where the perpetrator had the opportunity to help this person and was obliged to take care of him or he himself placed him in a state of danger to life or health, shall be punishable by a fine in the amount of up to 80 thousand roubles, or in the amount of the wage or salary, or any other income of the convicted person for a period of up to six months, or by compulsory labor for a term of 120 to 180 hours, or by corrective by work for a term of up to one year, or by arrest for a term of up to three months, or by deprivation of liberty for a term of up to one year.
The general sequence of first aid for road traffic traffic accidents are as follows:
- termination of further impact on the affected damaging factor;
- maintaining the vital functions of the victim's body;
- transfer of the victim to the ambulance team or delivery to a medical institution.
Assistance provided to victims of road accidents is divided into three stages:
- The first stage is at the scene of the accident. It includes pre-medical assistance to victims of road accidents, as well as, if necessary, self-help and mutual assistance. At the same stage, qualified medical assistance is provided by employees of ambulance teams and rescue services called to the scene. Our guide focuses on actions to help first aid at this stage by persons who do not have a special medical education;
- the second stage - when transporting the victims to a medical institution. This stage is usually carried out by medical or rescue special teams. However, in some cases, the delivery of victims to a medical institution can be carried out, for example, by drivers of passing vehicles. At this stage, the victims are also provided with the necessary assistance.
- the third stage - in a medical institution.
1. BRIEF INFORMATION ABOUT HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. THE MOST COMMON INJURIES DURING A RTA
In order to correctly determine the nature of the injuries received by the victims in an accident, it is necessary to know the basics of human anatomy and physiology.
The human body is made up of a number of organs. Their main integral part is a cell. Cells form tissues. Nervous, muscular, connective and integumentary tissues are distinguished. There are also systems in the human body: bone, muscle, digestive, respiratory, genitourinary, vascular, nervous, sensory organs, endocrine system and skin
.Each system performs a specific function, the activities of all systems are interconnected. Any harmful effect on one of the body systems is reflected in other systems, damaging the entire body as a whole. Such a harmful effect on the body of a person who has got into an accident is an injury. That is why, when providing first aid to a victim in an accident, it is necessary to take into account the interconnection of systems and the impact of injuries on the activity of the whole organism as a whole.
The human skeleton consists of all the bones of his body, and there are more than 200 of them. It serves as a support for the body, a solid foundation and protects the most important organs.
The surface of the bones is covered on top with a fibrous periosteum and contains numerous vessels and nerves. That is why fractures cause severe pain.
The skeleton consists of the skull, vertebral column, thorax, and bones of the upper and lower limbs. The spinal column is made up of vertebrae, which, stacked on top of each other, form a canal in which the spinal cord is located. The thorax is formed by twelve pairs of ribs and the sternum. The bones of the upper limbs include the clavicles, scapulae and the bones of the free part of the upper limb - the humerus, radius and ulna. The hand consists of the wrist, formed by eight carpal bones, and the metacarpus - by five metacarpal bones and phalanges of the fingers. The pelvic bone (pelvis) is formed by the ilium, ischium and pubic bones. The femur is attached to the pelvic bone. Further, the bones of the lower limb consist of the patella, the tibia and fibula (tibia), seven tarsal bones, five metatarsal bones and the phalanx of the toes.
Almost all the bones of the skull are firmly connected by sutures. Most of the bones of the skeleton are connected at joints, the surface of which is covered with cartilage. The joints are strengthened by articular bags and ligaments that hold the bones during movement.
Fractures are the most common type of bone injury in road accidents, and dislocations are somewhat less common.
The movement of the body occurs due to the work of the muscular system. Together with the bones, it forms the locomotor apparatus.
Muscles that attach to bones are called skeletal muscles and are controlled by willpower.
In addition to skeletal muscles, the stomach and intestines have visceral musculature, controlled by the autonomic nervous system, regardless of the will of the person.
There are over 300 muscles in the body. Muscle injuries in road accidents occur mainly only with deep wounds. As a result, the integrity of the muscles is disturbed, bleeding occurs, and the muscle partially or completely ceases to perform its function. In addition, in an accident, muscle bruises are possible, accompanied by hemorrhage and sprain.
Blood is a red, opaque liquid. She performs the most important features in human life support. The average adult human body contains 4-5 liters of blood.
Throughout a person's life, the blood in his vessels is in continuous motion. The heart is the main organ of blood circulation, which is a hollow muscle, divided by two atria and two ventricles (right and left) into two parts. It pumps up to 7000 liters of blood per day. In the human body, there are two circles of blood circulation: large and small.
The pulmonary circulation (pulmonary) is responsible for saturating the lungs with oxygen and releasing them from carbon dioxide. The pulmonary circulation begins in the right ventricle of the heart, from where blood flows through the pulmonary artery to the lungs, where it releases carbon dioxide and is saturated with oxygen. The oxygenated blood returns through the pulmonary veins to the left atrium. A large circle of blood circulation supplies oxygen to the entire body. It begins in the left ventricle, from where blood under pressure, called blood and due to the activity of the heart and the tension of the walls of blood vessels, along the main artery - the aorta - is carried throughout the body by vessels called arteries. The blood that has given up oxygen returns through the veins back to the right atrium of the heart. The smallest blood vessels are called capillaries.
In an accident, injuries that violate the integrity of the vascular walls are likely. As a result, bleeding occurs. With severe bleeding and severe injuries, a violation of blood pressure occurs and the victim, who has not received emergency assistance, may die. A sharp blow to the chest can cause cardiac arrest or damage. With a strong blow to the left side, a rupture of the spleen is possible.
The respiratory system is also one of the main life-supporting systems of the human body.
It begins with the nose, where the inhaled air is warmed and purified. Further, bypassing the nasopharynx, it enters the larynx, and then into the trachea, located in the chest. The trachea branches into the bronchi. Respiratory movements occur due to the movement of the diaphragm - the muscle that separates the chest from the abdominal cavity, as well as due to the movement of the intercostal muscles.
The most dangerous injury that a victim can receive in an accident is a stab wound with penetration into the pleural cavity. The penetration of air into this cavity causes the lungs to collapse and stop their activity. This condition is called pneumothorax. In addition, chest injuries and rib fractures are common injuries in road traffic crashes, which in certain cases can damage the lungs. Clogging of the larynx with vomit or retraction of the tongue in an unconscious victim can cause death by suffocation.
2. INITIAL ACTIONS AT THE SCENE OF A TRAFFIC ACCIDENT
If an accident occurs in which there are victims, then proceed according to the following general scheme:
2.1. Ensuring safety at the scene of an accident
Before proceeding with the provision of assistance, it is necessary to designate the scene by turning on the emergency light alarm and putting up an emergency stop sign. The warning triangle is installed at a distance of at least 15 meters from the vehicle in built-up areas and 30 meters outside settlements.
This must be done in order to protect the victims, as well as those who provide assistance to them. It is this sequence that is regulated by clause 2.5 of the SDA.
Your actions must be thoughtful. Ensure personal safety. car with gasoline engine burns out in 5 minutes. In this case, the threat of an explosion is real. Wrong actions can cost the life of not only the victim, but also those providing assistance. Always be alert at the scene of an accident. For example, if a car crashes into a pole, the power line wires may be broken. If this is not noticed, a person trying to provide assistance to persons in a damaged car, then there will be more victims and, perhaps, there will be no one to call an ambulance and (or) rescue service. Always assess the situation first. As professional rescuers say, it is better if there is one dead body than two as a result of the incident. It may sound somewhat cynical, but now we are teaching you to act thoughtfully, adhering to certain algorithms, and deviating from them can cost the life of not only the victim, but also the rescuer.
At the scene of an accident, to prevent the development of dangerous consequences, you should immediately turn off the car engine. Many modern vehicles are equipped with a special device that blocks the supply of fuel to the engine in case of an accident. If gasoline is spilled, be sure to disconnect the battery of the damaged car.
2.2. Calling ambulances and rescue services to the scene of an accident
You can call an ambulance and provide first aid at the same time. Although this will be possible in the case when several people can come to the rescue at once. In such a situation, it is also possible that one person indicates the scene of the incident, while the other at the same time, being in a safe zone, calls an ambulance. And then they begin to provide first aid. But if only one person can provide assistance, then you should always start with the designation of the scene. In a situation requiring urgent intervention, after marking the place of an accident, you may have to simultaneously provide assistance and call doctors and rescuers. That is why remember your mobile phone ambulance and rescue numbers so that you can call them using the speed dial function.
"03" is the traditional ambulance service number.
By calling "01" you can also call an ambulance and rescuers, although this phone was assigned to the fire department.
"0911" - a call from any cell phone to rescuers, police, ambulance, fire department, gas service.
"112" is an emergency channel of assistance in Moscow and in Europe, it is planned to introduce it throughout our country.
For more accurate information about emergency phone numbers, contact your network operator.
So, you got through to the ambulance service or rescue service. Now you need to speak quickly, but clearly. Be sure to indicate the number of victims in the accident, as a separate team is sent to each victim. You will be asked the following questions:
The number of victims and their gender;
- age, if you do not know - indicate approximately (child, teenager, adult, young, middle-aged, elderly);
- what happened (accident and condition of the victims in general terms, for example, unconsciousness, bleeding, etc.);
- address (maximum accuracy and landmarks for the entrance are important here);
- who is calling for an ambulance (leave your phone number as the crew may need to verify your location).
If the victims are trapped in damaged vehicles, then at the same time call the rescue service, you can also report this when calling an ambulance.
In our country, medical institutions are assigned to certain sections of roads, and appropriate road signs are installed on the highways, which indicate the nearest medical institution.
Qualified assistance to victims can also be provided by a doctor passing near the scene on private car. A special identification mark may be installed on his car. In some cases, when it is difficult for an ambulance or rescue team to reach the scene of an accident or the expected time of its arrival is too long, which can lead to the death of the victim, the driver is a participant in an accident who is able to drive his car (and the technical condition of the car allows it) must transport the victim to a medical facility. Or he can move towards an ambulance or rescue vehicle to transfer the victim. Although the most optimal in such a situation would be to transport the victim on any other vehicle passing by the scene of the incident.
3. EXTRACTION OF THE INJURED FROM THE VEHICLE
If as a result of an accident vehicle has received serious damage and its doors and windows do not open, try to open them with improvised means. In extreme cases, windows can be broken, but this should be done carefully so as not to cause additional injury to the victim. If the victim is pinched by the deformed parts of the vehicle, it is necessary to try to eliminate the traumatic factor. However, if it is obvious that this cannot be done, you should immediately contact the rescue service, whose specialized teams have all the necessary equipment to extract victims from damaged vehicles, or report this to an ambulance.
If the situation develops in such a way that the priority is to remove the victim as soon as possible, then this should be done as carefully as possible so as not to aggravate the severity of the injuries. Improper extraction of a person with damage to the cervical spine can lead to his death. Medical and rescue teams have a special neck collar for transporting individuals with such injuries.
When removing a person from a vehicle, in no case use forceful methods, that is, do not try to pull out parts of the body that are clamped by the elements of the car. First, free it from everything that prevents evacuation. If the victim is removed by at least two people, then, if possible, his posture should be maintained. If necessary, contact the drivers and passengers of passing vehicles. If you still have to remove the victim alone, then it is better to move him to the doorway so that you can sit behind him. Pass your hands through the victim's armpits and grasp the uninjured forearm of his arm. Then carefully remove it from the car.
Please note that in some cases it is possible to provide assistance to the victim right in the damaged car before the arrival of rescuers or ambulance staff. Evacuate him from the car only if possible consequences such actions will be less dangerous than leaving the victim in a damaged vehicle, for example, if there is a threat of fire or explosion.
You will learn more about how to carry and transport casualties in section 12 of this manual.
4. DETERMINATION OF THE CONDITION OF THE INJURY
4.1. Conscious victim
If the victim is conscious, the level of consciousness must be determined. To do this, ask him any question. Find out from him the places of localization of pain. Reassure the victim. Estimate the approximate severity of his injuries. Inspect it for injuries that are accompanied by dangerous bleeding. After helping such a victim, while waiting for the ambulance to arrive, talk to him without demanding answers. At such a moment, psychological support, distraction, and encouragement are very important.
A person injured in an accident is most often in a state of traumatic shock. Shock is a response of the body, characterized by a deep disorder of its functions. There are two phases of shock: excitement and then depression. When providing first aid, the victim should be freed from the traumatic factor, immobilized, given complete rest, warm, control the pulse and breathing. If possible, give painkillers (analgin, aspirin, pan dol). When the victim is in the first phase of shock, he may not be aware of the severity of his condition due to excitement. Then, if shock develops, there will be a sharp inhibition of all vital processes. The person becomes pale, motionless, does not complain of pain. Unlike fainting, consciousness is usually preserved in shock.
Fainting is accompanied by a short-term loss of consciousness. There is a sharp pallor of the skin, the eyes roll up and close, the victim loses his stable position. The limbs become cold to the touch, the skin becomes covered with sticky sweat, the pulse becomes rare. Possible involuntary urination. The duration of the attack ranges from a few seconds to 1-2 minutes, then there is a rapid and complete recovery of consciousness.
The victim in this state should be laid on his back with his head slightly thrown back, unfasten the collar, provide access to fresh air, spray his face with cold water, bring a cotton swab dipped in ammonia to his nose.
The victim needs to raise his legs: in this case, the blood will rush to the head faster, and he will soon regain consciousness.
4.2. The victim is unconscious
If the victim is unconscious, it is necessary to determine whether he is alive. This is very important, because often with serious injuries a person does not show signs of life. In such a situation, with the exception of undoubted signs of death, you should immediately begin to provide the necessary assistance.
If there is even the slightest doubt about the death of the victim, it is necessary to immediately take resuscitation measures in order to exclude the death of a person as a result of failure to provide assistance.
Consider the signs that allow us to conclude that the victim is undoubtedly alive.
The presence of a heartbeat is determined by ear or by hand. Listening is carried out (or put a hand) in the left side of the chest.
The pulse is most conveniently determined on the neck, in the region of the passage of the carotid artery, or on the temporal artery, or on the inside of the forearm.
The presence of breathing is determined by the reciprocating movements of the chest, as well as by the fogging of the mirror or by the fluctuation of cotton wool brought to the nose of the victim.
A sign that a person is alive is the constriction of the pupil when the eye is sharply illuminated, for example, with a flashlight. In his absence, a similar reaction can be achieved if the open eye of the victim is covered with a hand, and then the hand is quickly taken to the side.
Attention: with a deep loss of consciousness, the reaction to light may be absent.
In the presence of any of these reactions, emergency treatment can save a person's life.
5. RENDERING PRE-MEDICAL CARE TO A VICTIMS IN A STATE OF COMA
If a person is motionless, does not try to move, does not respond to sounds and painful stimuli, but breathes, then most likely he is unconscious. These signs give grounds to assume that the victim received a traumatic brain injury. It is usually accompanied by loss of consciousness (cerebral coma), and the state of the victim resembles a deep sleep. At the same time, the pulse on the carotid artery is preserved, and breathing becomes snoring with a wheeze on exhalation. The main danger of this condition is a sharp decrease in the tone of the hyoid muscles and the soft palate. The tongue, sticking to the back of the throat, completely stops air from entering the lungs. Check for a carotid pulse. If the victim is unconscious, but breathing and heartbeat are preserved, then he must be turned over on his stomach and constantly monitor the airway, breathing and heartbeat. The victim should be turned over as a whole, having previously fixed the cervical spine with hands or a special collar. Before the arrival of the ambulance, stay on the side of the face of the victim; if necessary, clean his mouth by wrapping his fingers with a handkerchief or napkin, control his breathing and pulse. In case of violation of these functions, immediately proceed to resuscitation.
6. RENDERING PRE-MEDICAL CARE TO A VICTIMS IN THE STATE OF CLINICAL DEATH
When breathing stops and the heart stops, death occurs. It is divided into two phases - clinical and biological. The duration of clinical death is 5-7 minutes. During this period, a person does not have breathing and heartbeat, but irreversible phenomena in the tissues do not yet occur. However, it must be borne in mind that in such a situation, the body is drastically lacking oxygen, which leads to the death of brain cells. In this regard, in the event of clinical death, all actions should be aimed at restoring the activity of the heart and lungs.
During this period, while there has not yet been severe damage to the brain, heart and lungs, a person can be brought back to life. After 8-10 minutes, biological death occurs and it will be impossible to save the victim. Therefore, the account goes in the literal sense of the second. When breathing and cardiac activity stop (a state of clinical death), the victim is laid on his back on a hard surface and his clothes are unbuttoned. Release him from everything that interferes with breathing. Having found the victim unconscious, it is necessary to ensure free airway patency and spend no more than 10 seconds to determine the presence of normal breathing. With a finger wrapped in a handkerchief or napkin, they clean the mouth and throat, check if the tongue has sunk. It is possible to turn the head of the victim to one side only if there is no suspicion of an injury to the cervical spine.
To avoid falling of the tongue, put a roller under the neck and shoulders. Next, the head of the victim should be thrown back strongly.
In some cases, after these manipulations, the victim may recover spontaneous breathing. This most often happens in cases where breathing was disturbed due to the impossibility of passing air through the nose and mouth.
If spontaneous breathing continues to be absent or ineffective, start artificial respiration. If it does not give results, then you should immediately start an indirect heart massage, or rather, cardiopulmonary resuscitation, with the technique of which we will get acquainted a little later. In the meantime, we will study the technique of performing artificial respiration.
It is carried out by one of the following mouth-to-mouth or mouth-to-nose methods. These methods make it possible to maintain life in a person, since the air exhaled by the rescuer contains up to 18% oxygen, and this oxygen will enter the blood of the person being assisted.
For mouth-to-mouth artificial respiration, use special device located in the car first aid kit.
As mentioned above, the victim must be prepared for artificial respiration. His mouth must be cleared of mucus, blood, food debris, etc. (if there is an artificial jaw, it must be removed). Next, you need to tilt the head of the victim to clear the airways. His chin should be in line with his neck.
After that, insert a special device from the first-aid kit into the victim’s mouth, if it is not there, then put a gauze bandage on the mouth and, after plugging the victim’s nose, start artificial respiration (16-18 breaths per minute).
Before you make artificial air blowing by the mouth-to-mouth method, including through a mask, you need to take a breath. Pinch the victim's nose and exhale vigorously until his chest begins to rise. Release your nose. Straighten up. Exhale the remaining air to the side. At this time, the victim makes an independent passive exhalation.
Blow air should be no more than one second. A long duration of air insufflation can reduce the return of blood to the heart and its filling with blood, which will lead to a decrease in cardiac output as a result of a series of subsequent chest compressions during cardiopulmonary resuscitation. It is necessary to monitor the tightness between the victim's mouth and the mouth of the rescuer at the moment of inhalation of air into the victim's mouth, as well as the tightness of his nose. After 3-5 breaths, check the carotid pulse.
If artificial respiration fails, chest compressions should be started immediately. The purpose of indirect massage is to squeeze blood from the heart into the arteries with each pressure on the chest. With the reverse movement of the hands, the heart is again filled with blood through the veins. Each pressure on the chest replaces one heartbeat. Chest compressions of at least 100 compressions per minute (except for newborns) can support life for several hours. Strong and fast pushes are recommended.
This should ensure complete decompression (return to normal) of the chest after each pressure. The duration of compression and decompression should be approximately the same. Try not to interrupt the closed heart massage unnecessarily. Every time you interrupt it, the circulation stops. Closed heart massage provides minimal blood flow to vital organs such as the brain and heart. The more correctly closed heart massage is performed (that is, with adequate frequency and depth of pressure and complete decompression), the more effective the blood circulation resulting from their implementation.
Before performing an indirect heart massage, the rescuer should place the palm of one hand on the lower third of the sternum (three fingers above the end of the sternum, approximately between the nipples), and the palm of the other hand on top.
The fingers of both hands should be raised, and the arms straightened at the elbow joints. Pressing is carried out mainly due to the weight of the person providing assistance. When pressed, the sternum of an adult is shifted to the spine by 4-5 cm.
For children up to a year, pressure is applied with two fingers, and for adolescents - with more care with both hands or with only one hand.
With proper indirect massage, its results may appear in a few minutes - constriction of the pupils and pinking of the skin. In this case, the massage should be continued until an independent pulse appears on the carotid artery or until the arrival of an ambulance. Often there is a need for cardiopulmonary resuscitation, that is, simultaneous artificial respiration and chest compressions.
If there is an assistant, then one of the rescuers performs artificial respiration, and the other performs chest compressions. In this case, a strict sequence of actions must be observed. It is unacceptable to simultaneously inhale and massage pressure.
In the absence of an assistant, it is necessary to carry out revival according to the system “two breaths - 15 chest compressions”. In this case, a compression-to-breathing ratio of 30:2 is recommended for all categories of victims, from infants (excluding neonates) to adults.
If only one person can provide assistance at the scene of the incident, and as a result of the incident, a child who is in a state of clinical death was injured, then after designating the scene of the incident, cardiopulmonary resuscitation should immediately begin. It is possible to be distracted in order to call an ambulance only after performing about five cycles of pressure and artificial ventilation (about two minutes).
After carrying out resuscitation of the victim, who is in an unconscious state, you should lay him on his side, placing his hand under his head, bend his free (upper) leg at the knee and put it on the ground.
7. PROVIDING FIRST AID FOR WOUNDS AND BLEEDINGS
Wounds - open injuries, accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the skin or mucous membranes, and in some cases even deeper lying tissues. Wounds are divided into cut, stab, chopped, torn, etc. They are usually accompanied by bleeding, which may be internal or external. Internal bleeding is accompanied by pallor of the skin, cold sweat, increasing weakness, loss of consciousness.
External bleeding is divided into:
Arterial - this is the most dangerous type of bleeding, since blood flows through the arteries from the heart under the greatest pressure. Arterial bleeding is easily recognized by a pulsating or even spouting stream of scarlet blood.
- Venous - with this type of bleeding, dark red blood is secreted by a continuous stream.
- Capillary - they are noted with a significant wound defect of the skin. The entire surface of the wound bleeds.
In case of damage to the arm or leg, it is most correct to cut the clothes. If this fails, then the clothing is first removed from the intact limb, and then, holding most of the clothing in the hands and manipulating it, carefully remove it from the injured limb.
7.1. Providing first aid for arterial bleeding
Arterial bleeding must be stopped as soon as possible, since the life of the victim often depends on it. The average blood volume in an adult is about 4-5 liters. The loss of 1/3 of the blood volume in a short time usually leads to death.
The first step is to clamp the artery that supplies the wounded part of the body with blood. To temporarily stop arterial bleeding, the artery is pressed in places where it is located superficially, that is, close to the skin. In these places, you can usually feel the pulse. The artery is pressed with several fingers 2-3 cm above the wound (closer to the body).
For transportation, it is usually necessary to apply a hemostatic tourniquet or twist. The imposition of a tourniquet in almost all cases allows you to stop arterial bleeding.
The car first-aid kit also has a tourniquet to stop arterial bleeding with dosed compression (squeezing). It can be replaced with a belt, belt, suspenders, etc. A tourniquet is applied to the limb above the site of bleeding with two or three turns, and only on top of the clothes or under it is a lining made of a bandage folded in several layers, a scarf, a towel, any matter.
The tightening of the tourniquet is stopped at the moment the bleeding stops. A note must be attached to the tourniquet indicating the time of its application. Since the tourniquet stops the access of blood to the tissues, it can only be applied for a limited time: in winter - no more than 0.5 hours, in warm weather - no more than 1 hour. After this period, if the victim did not have time to be hospitalized, it should be dissolved burn for up to five minutes, and then repeat this procedure every 30 minutes. After each dissolution of the tourniquet, it is necessary to indicate in the note the new time of its application. By the way, the note may get lost during transportation, so the rescue service staff recommend duplicating the inscription on the victim's forehead. This, of course, is unusual, but it is better to convey information in this way than not to convey it at all.
With a short-term dissolution of the tourniquet and before applying it, use methods to temporarily stop bleeding.
If a tourniquet is applied to stop arterial bleeding that has arisen from a limb amputated as a result of an accident, then the tourniquet must not be loosened. At the same time, it should be applied approximately 5 cm above the injury site.
As already mentioned, in the absence of a tourniquet, a twist can be used to stop arterial bleeding, which is made from a scarf, scarf, bandage, etc.
Cords, ropes and other narrow inelastic materials are not allowed as a substitute for a tourniquet.
The imposition of a tourniquet (twist) in other cases should be used only under extreme circumstances. Since most often the imposition of a tight bandage and finger pressure on the arteries is sufficient to stop severe bleeding. The first aid provider should be aware that applying a tourniquet to a non-amputated limb cuts off blood flow to areas below the tourniquet, which can damage nerves, blood vessels, and ultimately loss of the limb.
7.2. Providing first aid for venous and capillary bleeding
With venous bleeding, a pressure bandage is applied to the wound site.
Before applying a bandage, it is necessary to treat the skin around the wound with tincture of iodine, close the wound with a sterile napkin, and apply a sealing roller along the top of the bones. After that, tightly bandage the wound and give the limb an elevated position.
A sign of the correct imposition of a pressure bandage is the cessation of bleeding (the bandage should not be saturated with blood).
Currently, all motor vehicles, with the exception of motorcycles without side trailer must be equipped with a first aid kit. For the treatment of wounds (in the absence of damage to the arteries), use the dressing bag available in the first-aid kit. Bactericidal wipes "Coltex GEM" with furagin are designed to stop capillary and venous bleeding. Atraumatic dressing MAG with dioxin or silver nitrate is intended for wound dressing. The wound must not be washed with water. Wipe the skin around it with a solution of iodine or brilliant green. If you have a bactericidal napkin, without treating the wound, cover the wound completely with a napkin and fix it with adhesive plaster or bandage.
7.3. First aid for penetrating chest wounds
Penetrating wounds of the chest can be associated with damage to vital organs (lungs and heart), and internal hemorrhage is also possible. The greatest danger is created by air entering the pleural cavity, which leads to the development of pneumothorax.
Pneumothorax is accompanied by a characteristic noise and whistling when air enters and leaves the wound. First aid for penetrating chest wounds is to protect the wound from infection, eliminate the developed pneumothorax and prevent possible shock.
For penetrating chest wounds, immediately apply a sealing bandage. For this, you can use adhesive tape, a plastic bag or oilcloth. Pretreat the skin around the wound with iodine or brilliant green solution. Fix the bandage while exhaling. Such a victim is transported sitting.
If there is a foreign object in the wound, it cannot be removed. If the object sticks out, it is fixed as much as possible and a bandage is applied around it. This applies not only to cases of penetrating wounds of the chest, but to any wounds.
7.4. Providing first aid for head injuries
With head injuries, it is first necessary to stop the bleeding and prevent secondary infection from entering the wound. Hair at the scene of an accident is not cut. A sterile napkin is applied to the wound, then a thick layer of cotton wool and all this is fixed with one of the special dressings.
It should be borne in mind that in case of injuries associated with head injuries, the victim may have brain damage (possibly a concussion or bruise of the brain). Therefore, after applying a fixing bandage, the victim should be laid on his back, turning his head to the healthy side.
If the victim is unconscious, then he is laid on his side and transported in the same position.
7.5. Providing first aid for nosebleeds
The danger of profuse nosebleeds is a violation of breathing due to the penetration of blood into the respiratory tract. To prevent this from happening, the victim's head is tilted forward, and cold is applied to the nose in the region of the bridge of the nose.
7.6. Providing first aid for abdominal injuries 7.6.1. Penetrating wounds of the abdomen
With a penetrating wound of the abdominal wall, damage to the internal organs of the abdominal cavity occurs. When the intestine is injured, its contents enter the abdominal cavity, which can lead to purulent inflammation of the peritoneum (peritonitis). First aid is aimed at protecting the wound from infection and saving the fallen organs. Dropped internal organs should be carefully collected in a damp cloth and placed in a bag. The package must be glued to the body of the victim with adhesive tape, plaster or bandaged without pinching. The intestines can be touched - it is painless for the victim. The bandage must be constantly moistened - so that the intestines do not dry out. Apply a sterile napkin to the wound, then a thick layer of cotton wool and make a tight (non-tight) bandage. The position of the body during transportation - lying on your back, place a roller under your legs bent at the knees.
A victim with a penetrating wound of the abdomen should not be allowed to drink, try to set the fallen organs into the abdominal cavity.
7.6.2. Closed injuries of the abdominal cavity
Closed injuries of the abdominal cavity occur with bruises and compression.
Signs: acute pain in the abdomen, nausea, vomiting, etc. First aid is aimed at creating rest and reducing the risk of possible internal hemorrhage.
The position of the body with closed injuries of the abdominal cavity - lying on its side with legs bent at the knees or half-sitting with legs bent at the knees. Put cold on the stomach for 20 minutes.
7.7. Providing first aid for traumatic amputation
The amputated limb should be placed in a bag, then this bag should be placed in another and cooled. Provide the victim with the necessary assistance. If the amputation caused arterial bleeding, a tourniquet should be applied (see section 7.1). The amputated limb package should be shipped with the casualty. When calling an ambulance to the scene of an accident, it is imperative to say that the victim has had a limb amputated. Within six hours from the moment of amputation, there is a chance for a successful operation to restore the lost limb.
8. PROVIDING FIRST AID FOR BRUISES, DISTRUCTIONS AND FRACTURES
8.1. Help for bruises
A bruise is a closed injury to soft tissues and blood vessels with the formation of bruises. They occur when hitting a blunt hard object.
Signs: pain that appears at the time of the bruise, or swelling shortly after the bruise, which may be restrictive and vague; bruise or hematoma, depending on the depth of the injury.
First aid is aimed at reducing hemorrhage and relieving pain. The bruised limb should be elevated and, if possible, tightly bandaged to reduce internal hemorrhage. Cold is applied to the site of injury for 1.5-2 hours, then heat. For cooling, you can use a cold compress, a bubble with ice, snow, cold water, as well as a hypothermic (cooling) container package available in the first aid kit. To relieve pain, a bruised organ is given rest. For example, a hand can be hung on a scarf, a bandage can be applied to a joint, etc.
With injuries accompanied by a bruise, fractures are possible. Therefore, during the period of pre-medical care, it should be treated as a fracture.
8.2. Assistance with dislocations
Dislocation - the exit of the head of one bone from the joint bag of another, accompanied by a rupture of the joint bag. Signs of dislocation - swelling and pain of movement in the joint, its deformation. Only a doctor can set the bones that have come out of the joint. In addition, dislocation may be accompanied by cracks and fractures of the bones. Before the doctor arrives or before the victim is delivered to the doctor, the limb should be immobilized in the position in which it was after the dislocation, and cold should be applied to the joint.
In case of dislocation of the wrist joint, a roller should be placed in the hand, a single splint should be applied and the arm bent at the elbow should be hung on the sling. In case of dislocation of the shoulder joint, you should hang your hand on a scarf or bandage it to the body.
In case of dislocation of the ankle joint, an eight-shaped (cruciform) bandage is applied.
In case of dislocation of the knee joint, fixation is carried out by the so-called tortoise bandage.
8.3. Help with fractures
The unnatural position of the victim, the deformation of the limbs indicate bone fractures. In this case, you can not move the victim even a short distance. Movement can lead to displacement of bone fragments, increased bleeding, and deepening of shock. Only in the event of a risk of explosion, fire, etc. the victim is transported with extreme care. Damaged limbs must be immobilized (immobilized), fixed by any available means.
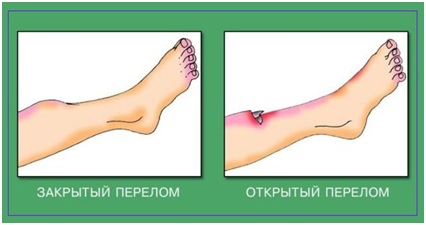
Fractures are divided into closure and open.
Closed fracture - a traumatic violation of the integrity of the bone without violating the integrity of the skin. It is characterized by an unnatural shape of the limb, swelling, redness, pain.
When providing first aid, it is necessary to immobilize a broken bone with bandages or splints.
Tires should capture the fracture site and 2-3 nearby joints. Immobilization of broken limbs is carried out using standard splints or improvised means.
An open fracture is a traumatic violation of the integrity of the bone with a violation of the integrity of the skin. We deal with such a fracture at first as with a wound.
If necessary, to stop arterial bleeding, a tourniquet or twist is applied above the fracture site with a note about the time the tourniquet was applied. The skin around the wound is treated with an alcohol solution of iodine or brilliant green. The wound is closed with a sterile dressing. The broken bone is immobilized in the position that it took as a result of the fracture. Bone fragments are not reduced.
8.3.1. Assistance for a broken jaw
In case of a fracture of the jaw, a sling-like bandage is applied.
8.3.2. Treating fractures of the shoulder, forearm and collarbone
In case of a fracture of the bones of the shoulder, a special Cramer metal splint is used, which is part of the medical equipment of the traffic police posts.
In its absence, do this: put a light fabric pad in the armpit; carefully place the broken arm along the body, the forearm at a right angle across the chest; put two tires (can be made from improvised materials, even newspapers and magazines will do) on the inside and outside of the shoulder; fix the arm in a bent state with a scarf bandage.
In case of a fracture of the forearm, a roller should be placed in the victim's hand, a single splint should be applied and the arm bent at the elbow should be fixed relative to the body.
In case of a fracture of the collarbone, you should hang your hand on a scarf and bandage it to the body.
If there is a suspicion of a fracture of two clavicles at once, then to assist, straighten the chest, bring the shoulder blades together behind.
This can be achieved different ways: using rings or tying hands at the elbows behind the back. Insert rollers into the armpits.
8.3.3. Help with broken ribs
With this injury, a tight bandage should be applied to the victim. Fixation is made at the moment of exhalation.
The victim with fractures of the ribs and sternum is transported sitting or reclining, placing a roller under the knees. In the same position, he must be while waiting for the arrival of an ambulance.
8.3.4. Assistance for a fracture of the tibia
In case of a fracture of the lower leg, two splints are applied from the outer and inside legs from the end of the foot to the middle of the thigh. It is necessary to fix two joints located above and below the fracture site. When splinting the shin and thigh, the foot must be fixed at an angle of 90° to the shin. You can not fix the toes in a straightened position. Immobilization of the injured limb standard tires or hand tools.
8.3.5. Assistance with fractures of the hip and pelvic bones
A hip fracture requires two splints. One tire on the outside from the end of the foot to the armpit, the other on the inside from the end of the foot to the groin.
If in case of a fracture of the lower leg and thigh there are no immobilization agents, the diseased leg is fixed to the healthy one. The fixing bandage should not displace bone fragments and cause additional pain to the victim. It must be applied to the healthy part of the leg.
In case of a fracture of the pelvic bones, the victim is laid on a hard surface, a roller is placed under the legs bent at the knees.
In this position, the victim is transported to a medical facility.
8.3.6. Assistance for spinal fractures
If a spinal injury is suspected, the victim should be placed on their back or stomach on a hard, flat surface.
9. RENDERING FIRST AID FOR DROWNING
If the car has fallen into water, do not leave it until it is completely immersed in water.
Close all windows immediately, turn on the headlights, they will be able to work for some time and serve as a guide for rescuers.
Lower the seatback to make room for movement. Determine if there are watercraft in the car that will help you get to the surface. Get rid of heavy clothes and shoes.
When the water almost fills the cabin, it will be easy to open the door, but if it is jammed, it is necessary to break the glass and evacuate through the window.
If you have to help someone who has drowned or is drowning, then you need to act in a certain sequence. A drowning person is characterized by convulsive, uncoordinated movements, so you need to be very careful when pulling him out of the water. Swim up to the drowning man from behind and, grabbing him by the hair or armpits, turn him face up.
Since drowning is the closure of the respiratory tract with water, mud, silt, etc., the first aid is aimed at eliminating the main cause of suffocation, restoring breathing and cardiac activity.
On the shore, quickly release the victim from the clothes that are constricting him and clean his mouth and throat.
Then fold the casualty over the assister's thigh so that the head is lower than the torso. Press vigorously between your shoulder blades to remove water from your airways and stomach.
Lay the victim on his back, rub, cover, warm.
In the absence of breathing and cardiac activity, perform artificial respiration and chest compressions.
After the restoration of breathing and cardiac activity, heat, a warming drink (tea, coffee) are shown.
Let the cotton swab moistened with ammonia be smelled. Then the victim must be taken to a medical facility.
10. FIRST AID FOR CARBON MONOXIDE POISONING
Such poisoning occurs most often not as a result of an accident, but when you are in poorly ventilated rooms at work, with drivers of faulty cars, in a garage.
Exhaust gases contain more than 200 chemical compounds harmful to human health. The car engine consumes not only fuel, but also atmospheric air. One car per year, on average, absorbs more than 4 tons of oxygen from the atmosphere, while emitting approximately 800 kg of CO (carbon monoxide), 40 kg of nitrogen oxides and almost 200 kg of various hydrocarbons with exhaust gases. If the engine is incorrectly adjusted, the content of harmful substances can increase by 3-5 times, while engine power decreases and fuel consumption increases. The driver must regularly check whether the fuel is completely burned in the engine cylinders and whether the carbon monoxide content does not exceed the established norms. Such verification and, if necessary, adjustment can be carried out at stations Maintenance or at mobile environmental control posts.
The characteristic signs of carbon monoxide poisoning are headache, dizziness, tinnitus, nausea, and vomiting. In addition, drowsiness appears, which most often leads to the death of a person, since he is unable to leave the gassed room. With further inhalation of toxic substances, convulsions begin and death occurs from paralysis of the respiratory tract.
Having found such a victim, immediately take him out of the zone of action of toxic substances.
Maximize the intake of fresh air.
Release the victim from all tight and impeding free breathing clothes.
If shallow breathing is weak or stops, begin artificial respiration as soon as possible until steady spontaneous breathing appears.
11. PROVIDING FIRST AID FOR BURNS
As a result of an accident, victims can receive thermal, chemical or electrical burns.
Thermal burns occur from direct exposure to high temperatures (the flames of a burning car and fuel, hot antifreeze, etc.).
Chemical burns are the result of exposure to acids, alkalis (when the battery is destroyed).
Electrical burns are formed from the effects of electric current (in case of accidents associated with collisions with lighting towers or power lines).
11.1. Thermal burns
Before proceeding with the provision of assistance, it is necessary to stop the impact on the affected damaging factor. It should be borne in mind that the severity of the lesion depends on the temperature, duration and area of exposure. The larger the area of the burn and its depth, the greater the danger it poses to the life of the victim. Burning 1/3 of the body surface often leads to death.
Depending on the depth of the lesion, burns are divided into four degrees:
- For I degree is characterized by redness of the skin, swelling, pain. The burn site should be treated with cold water, then with an anti-burn ointment and a sterile dressing should be applied. The burn must not be treated with oil or ointments!
- Grade II is characterized by the formation of blisters filled with a clear or yellowish liquid. They should not be pierced, cut, or placed under cold running water to avoid infection. The burn site should be treated with an anti-burn ointment or synthomycin emulsion.
- With a third-degree burn (necrosis), a scab is formed on the skin, thin or dry, whitish-brown in color or large blisters with bloody fluid. Pain sensitivity at the burn site is reduced or absent. The burn site must be covered with sterile material.
- At the IV degree, charring occurs.
When calling an ambulance, it is necessary to inform the dispatcher that there are victims with burns.
If clothing is on fire, do not try to extinguish the flame by running. In order to extinguish the fire, it is necessary to stop the access of air. To do this, cover the victim with a tarp, blanket or coat. Remove (cut off) those parts of the clothing that are peeling off. Adhering clothing must not be torn off. Apply a dry sterile bandage to the affected areas. For extensive burns, wrap the victim in a sterile sheet.
It is impossible: to cover the head of the victim with a tarpaulin, to remove areas of clothing that have stuck to the burn site. A sterile bandage should be applied over these areas of clothing, applied with ointments and treated with any liquids. If vomiting occurs, lay the victim on their side. In the absence of vomiting, give a large salt drink (1 teaspoon of salt per 1 liter of water), provided that there is no damage to the internal organs.
11.2. Chemical burns
With acid burns, a limited yellow spot remains on the skin. Wash it with water tangentially to the surface of the burn, then neutralize with a slightly alkaline solution (soap or soda solution) and cover with a sterile dressing. Burns caused by concentrated sulfuric acid (dark brown spot) should not be washed with water. The affected part of the body should be treated only with a soap or soda solution.
Give the victim an alkaline drink: 1 teaspoon of baking soda in 1 glass of water. If the electrolyte comes into contact with the face, wash the affected area tangentially to the nose as shown in the figure. Then put 2 drops of sodium sulfacyl into the eyes.
With alkaline burns, a loose gray spot is formed. Rinse tangentially with water and neutralize with a slightly acidic solution (boric, acetic or citric acid solution). Close with a sterile bandage.
11.3. electrical burns
As already mentioned, electric shock can occur during accidents associated with collisions with lighting masts or power lines, as well as during a lightning discharge. Before rendering assistance, it is necessary to release the victim from the action of electric current. In case of electric shock with a voltage of less than 1000 V, the wire that was the source of the damage should be de-energized. To do this, if it is impossible to de-energize the line, cut the wire with a tool with a dry wooden handle, bite with wire cutters with insulated handles (each phase separately).
If it is not possible to quickly de-energize the wire, the rescuer must take precautions. Use rubber shoes, a mat from a car or camera, dry boards, dry clothes, gloves, a dry wooden stick, a dry cloth or jacket that wraps your hands. Use a non-conductive object to remove the wire from the victim.
If the victim is struck by a current of more than 1000 V, it is necessary to use dielectric gloves, rubber boots, a special insulating rod designed for the corresponding voltage.
Local changes are manifested by burns ("current points") at the points of contact with the current-carrying wire. Apply dry sterile dressings to the burned areas. General changes occur when current passes through the body: nervous regulation is disturbed and tonic muscle contraction occurs.
If the victim is in a state of "clinical death", he needs to carry out artificial respiration and chest compressions.
12. TRANSPORTATION AND TRANSPORTATION OF VICTIMS
As already indicated, the movement of victims by non-specialists should be carried out only in case of emergency and in such a way as not to create an additional threat to the wounded. The method of moving and shifting is selected depending on the nature and location of injuries, the condition of the victim, the number of people who can provide assistance and their physical capabilities, and also depending on the availability of improvised means.
12.1. Transfer of casualties
12.1.1. Independent movement
If the victim has no contraindications, that is, if there are minor injuries, he can move independently, leaning on the hand of the accompanying person.
In more severe cases, the rescuer puts the victim's hand on his shoulders, with one hand grabs the wrist of this hand, and the other grabs the victim by the waist. If the victim cannot move independently, he must be carried by hand or with the help of improvised means.
12.1.2. Carrying an injured person by one rescuer
The transfer of the victim by one rescuer is carried out on the shoulder, arms or back.
An unconscious victim is carried on the shoulder, if he has no contraindications to such a movement.
When carrying the victim on his hands for short distances, it is convenient to make an impromptu soft fabric seat for him. In this case, part of the load is transferred from the hands of the rescuer to his torso.
When carrying the victim on his back, the rescuer holds him by the hips. The victim is holding onto the rescuer's neck. When carrying on the back, it is convenient to use a shoulder strap or two waist belts.
12.1.3. Carrying the victim by two rescuers in their arms
To transfer the victim in the hands of two rescuers, the so-called locks from the hands of rescuers are used.
Two handed seat. A ring is made from a towel, cloth, rope, for which the rescuers hold. They can move straight, supporting the victim with their free hands.
"Castle" of three hands. One rescuer wraps his right hand around his left forearm, and with his left hand - the right forearm of the second rescuer. The second rescuer with his right hand takes the right forearm of the first rescuer, with his left hand he supports the victim.
"Castle" of four hands. Each rescuer holds his left forearm with his right hand, and the other rescuer's right forearm with his left hand.
This method is used when the victim is conscious and can hold on to the rescuers' necks.
12.1.4. Transfer of the victim with the help of improvised means
Straps, belts, a chair and two poles, a pole and sheets can be used as improvised means.
12.1.5. Carrying an injured person on a stretcher
This way of carrying is the most convenient and safe. In the absence of standard stretchers, they can be made from improvised means.
It is important to correctly place the victim on a stretcher so as not to cause him additional injuries and unnecessary pain. It is desirable that the victim was placed on a stretcher by at least two rescuers. When lowering the casualty onto the stretcher, both rescuers should kneel and carefully place the casualty down.
In case of a leg injury, immobilization of the limbs must be carried out.
In order to transfer the victim to the stretcher, the rescuers stand over the victim and lift him between their legs. When carrying a victim on a flat surface, rescuers should move in short steps, out of step, to prevent unnecessary shaking. In this case, the victim should lie with his feet forward, and the rescuer standing at the head should monitor the condition of the victim.
When moving uphill (for example, up stairs), the victim must be carried head first, and when descending, feet first. However, victims with serious injuries of the lower extremities should be transported in the reverse order: on the ascent - feet first, on the descent - head to ensure the most comfortable condition of the injured legs.
12.2. Transportation of victims
Transportation of road accident victims is carried out mainly by specially equipped ambulances and rescue services, and in some cases by medical helicopters. However, a situation may arise when the victim will have to be transported to a medical institution by passing transport.
12.2.1. Transportation in case of head injury
Before transportation, such a victim is laid on his back, turning his head to the uninjured side. If the victim is unconscious, then he is transported lying on his side, since with this injury vomiting is possible and the vomit must not enter the respiratory tract.
12.2.2. Transportation in case of chest injury
With closed injuries, transportation is carried out half-sitting with legs bent at the knees. With penetrating wounds, after providing appropriate assistance, lying on the wounded side.
12.2.3. Transportation in case of abdominal trauma
With closed and open injuries of the abdominal cavity, the trunk can be in the following positions:
- 1. Lying on your back with your legs bent. Turn your head to the side, put a roller under your knees.
- 2. Lying on a healthy side with legs bent at the knees (in the absence of consciousness).
12.2.4. Transportation in case of damage to the pelvic bones
Body position - lying on your back, on a flat hard surface. Place a roller under the legs bent and spread apart at the knees or place an emphasis at the feet. This position of the body helps to relax the muscles, and therefore, reduces pain, and is an anti-shock measure.
12.2.5. Transportation in case of spinal injury
The injury most often occurs as a result of a blow against a hard object or as a result of a blow with a blunt object to the back. The victim falls on his back or stomach. The position of the body is extended. Maintain immobility in the position in which the victim lies. Don't flip!
Transport lying on your back or stomach (as it lies) on a hard, even shield. Fix the body.
12.2.6. Transportation in case of injuries of the lower extremities
For lower limb fractures, first immobilize the broken bones with standard or improvised splints.
In case of a fracture of the lower leg, apply two splints from the end of the foot to the middle of the thigh. The foot is fixed at an angle of 90° to the lower leg.
In case of a fracture of the femur, apply two splints from the inside and outside: one from the end of the foot to the armpit, the second from the end of the foot to the groin. Only after this, the victim can be transported in the supine position (on the shield). Fix the body.
12.2.7. Transportation in case of injuries of the upper limbs
Transportation with these injuries is carried out in a sitting position.
13. CAR MEDICAL KIT
In accordance with the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated September 8, 2009 No. 97 of Moscow “On Amendments to the Order of the Ministry of Health and Medical Industry Russian Federation dated August 20, 1996 325 "from July 2010, the production of new car first-aid kits should begin.
Samples of first-aid kits issued earlier are valid until the expiration date, but no later than December 31, 2011.
1. The means that are part of the first aid kit (car), when providing first aid to persons injured as a result of road traffic accidents, are recommended to be used as follows:
- a) when providing first aid to persons injured as a result of traffic accidents, perform all manipulations with medical gloves;
- b) in case of arterial bleeding from a large (main) artery, press the vessel with your fingers at the pressure points, apply a hemostatic tourniquet above the injury site, indicating in the note the time of applying the tourniquet, apply a pressure (tight) bandage to the wound;
- c) if the victim does not have spontaneous breathing, perform artificial respiration using the device for artificial respiration "Mouth-Device-Mouth";
- d) if there is a wound, apply a pressure (tight) bandage using sterile napkins and bandages or using a sterile dressing bag. In the absence of bleeding from the wound and the absence of the possibility of applying a pressure bandage, apply a sterile napkin to the wound and fix it with adhesive tape. For microtraumas, use a bactericidal adhesive plaster.
Currently, almost all vehicles are equipped with old-style first-aid kits that are valid until December 31, 2011 (provided that the expiration date of the funds included in it has not expired by this date). It should also be noted that the approved new composition of the first aid kit is designed to provide first aid for injuries and life-threatening conditions. At the same time, the driver has the right, at his own discretion, to store in the first-aid kit other medicines that are freely available in pharmacies. Therefore, those medicines that were in the old first-aid kit, it is quite possible to continue to carry them with you.
- Painkillers, anti-inflammatory and anti-shock drugs for injuries, wounds, shock: analgin, aspirin, sodium sulfacyl solution, portable hypothermic (cooling) container bag.
- Means for stopping bleeding, treating and dressing wounds: tourniquet to stop bleeding, sterile and non-sterile bandages, bactericidal wipes or antimicrobial dressing, statin, bactericidal adhesive plaster, iodine or brilliant green solution, adhesive plaster, elastic tubular bandage, cotton wool.
- Remedies for pain in the heart: validol, nitroglycerin.
- Means for cardiopulmonary resuscitation in clinical death: a device for artificial respiration.
- Means for detoxification in case of food poisoning: activated charcoal or enterodesis.
- Remedy for stress reactions: Corvalol.
- Scissors.
Mesh-tubular bandages are available in seven sizes, according to the volume of various parts of the body.
- Bandage No. 1 is applied to the fingers, hands of adults, the hand and foot of children; in the free state, its diameter is 10 mm.
- Bandage No. 2 is applied to the hand, forearm, foot, elbow, wrist, ankle joints of adults, to the shoulder, lower leg, knee joints of children; in the free state, its diameter is 17 mm.
- Bandage No. 3 and 4 is applied to the forearm, shoulder, lower leg, knee joint of adults, to the thigh and head of children; in the free state, its diameter is 25 and 30 mm.
- Bandage No. 5 and 6 - on the head, thigh of adults, on the chest, abdomen, pelvis, perineum of children; in the free state, its diameter is 35 and 40 mm.
- Bandage No. 7 - on the chest, abdomen, pelvis, perineum of adults; in the free state, its diameter is 50 mm.
In order to apply a bandage, a hand or fingers are passed inside, depending on the size of the bandage, both hands stretch it, put it on the body and take out the hands. The bandage shrinks and tightly covers the area.
Bandages can be reused after laundering. Since they are destroyed by acids, alkalis, oils, it is not recommended to use synthetic detergents. Dry the bandages without squeezing, without twisting. You can cut off the desired part from the bandage, while the bandage does not dissolve.
Bandage bandages. Bandaging rules
To avoid causing unnecessary pain, support the injured body part while bandaging. The victim should be in a position convenient for him, so that during bandaging he does not change his posture from fatigue.
The bandaged part of the body should be in the position in which it will be after bandaging.
The one who provides assistance usually stands facing the patient in order to follow the expression on his face.
The bandage is kept in right hand roll up.
Bandaging starts from the bottom up. The bandage is held with the left hand and the bandage moves are smoothed out.
The bandage is rolled out without tearing it from the surface of the body from left to right with a subsequent turn, covering the previous one by 1/2 or 2/3 of its width.
When bandaging the limb, the fingers are left free, the bandage is applied not very tight, but not very weak.
Bandaging should begin with the fixing stroke of the bandage.
At the end of the dressing, the bandage must be fixed in a healthy place.
A well and correctly applied bandage bandage should: cover a completely diseased area of the body, do not disturb lymph and blood circulation, and be comfortable for the patient.
Adhesive bandages
We have already said that for minor wounds, cuts and scratches, you can use a bactericidal adhesive plaster, which covers the directly damaged surface. The side of the pad that is in the center of the adhesive tape is designed to come into contact with the damaged surface. This pad is covered with a micro-mesh that quickly passes and distributes secretions. At the same time, the coating itself remains dry and prevents the pad from sticking to the wound. The pad is impregnated with a special substance - ac-rinol, which has antimicrobial activity. Such patches can be made on a polymer, non-woven or fabric basis.
When dressings, it is convenient to use a roll adhesive plaster. It adheres well to dry skin and is convenient for fixing various dressings and for sealing small wounds. A rolled adhesive plaster is also used when it is necessary to bring the edges of the wound together and hold them in this position, as well as when applying bandages for traction. This patch is indispensable for sealing wounds in pneumothorax, which occurs with penetrating wounds of the chest. To apply such a bandage, you need to take a piece of adhesive plaster that is larger than the wound. The first strip is applied at the lower edge of the wound, bringing its edges closer. The second strip of plaster and each subsequent one is glued so that they overlap the previous ones by about 1/3 of the width, like roof tiles. Such a bandage is called "tiled", because. its overlay is like covering a roof with tiles.
For sealing small abrasions, medical glue BF-6 and furoplast can be used. They are applied in a thin layer to the wound. When they dry, a thin film is formed that protects the wound from infection.
Unfortunately, road accidents are a frequent occurrence, and everyone has seen an accident at least once in their life. Most deaths in road accidents occur due to untimely or inept first aid.
First aid in case of an accident
There is a certain scheme of actions aimed at saving a person who got into an accident. The algorithm is the following:
- Determining the nature of the injury and its source. In most cases, there are craniocerebral injuries, damage to the limbs and the chest area.
- Removal of the victim from the car.
- Liberation of a person from clothes.
- First aid.
- Transferring the victim to a calm, warm, safe place, shelter from the weather.
- Call an ambulance.
- Transportation of the victim to a medical institution (escort in an ambulance).
If the injuries are life-threatening or the person does not regain consciousness, one must be extremely careful and seek the advice of experienced medical professionals. Sometimes transporting a person can only worsen the condition (internal bleeding will occur, injuries will worsen, breathing will stop).
The rescuer should first evaluate the following factors:
- Identify life-threatening circumstances.
- Determine the presence of arterial bleeding.
- Check for respiratory problems.
- Determine cardiac arrest.
- Identify secondary hazards (burns, injuries).
If a person has lost consciousness, he has no heartbeat and breathing, then you need to do the following:
- Free up the airways.
- Make artificial respiration.
- Do a heart massage.
- Bring the person back to consciousness (give ammonia a sniff).
Removing the victim from the car
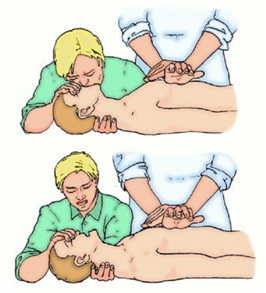 Both the driver and the passenger in the front or rear can be injured during an accident. back seat. The technique for extracting a person who is conscious and unconscious is different.
Both the driver and the passenger in the front or rear can be injured during an accident. back seat. The technique for extracting a person who is conscious and unconscious is different.
The algorithm of actions when extracting the victim through the front door (the person is conscious):
- open the door;
- under the armpits, first with one, then with the other hand, grab the forearms;
- pull a person out of the car;
- the second rescuer must grab the person by the legs;
- move the person to a comfortable place.
The technique for extracting the victim through the front door when the person is unconscious is similar to the first option, however, when grabbing the forearms, it is also necessary to secure the head by holding the chin.
To remove the victim through back door, the algorithm of actions is similar. If the spine is damaged, several rescuers remove the person, pulling him by the head.
If there is a suspicion of a spinal injury, the person is placed on a hard, flat surface. If a person has no injuries, but he has lost consciousness, then a lateral stable position is observed. If there are injuries to the abdomen or pelvis, then the person is laid on his back, the legs are bent at the knees, and a soft support is placed under the back.
If a person has lost a lot of blood, he is placed on a soft bed on his back, his legs are raised. If the chest is injured, then the person is placed on his side with a bias towards the injury.
First aid: different cases
Before providing first aid, you need to assess the condition of the person. 70% of road traffic deaths are due to improper first aid. 10% of the patient's life depends on how quickly the ambulance arrives. Only 20% of deaths are due to serious injuries.
Normally, a person should have up to 20 breaths per minute. After an accident, the breathing rhythm may go astray and fluctuate between 8 and 30. The pulse should be 60 to 80 beats per minute, in a state of shock, the indicators may slightly change up or down.
Despite the state of shock, the pupils should respond to light (expand). If no changes occur, the condition is life-threatening.
You also need to examine the skin. They should be pink and warm. If the person is unconscious, the skin will be pale and cold.
clinical death
 Clinical death can be determined by the following signs:
Clinical death can be determined by the following signs:
- loss of consciousness;
- lack of heartbeat;
- dilated pupils.
First aid for clinical death includes the following actions:
- put the person on a hard, flat surface;
- pull out the tongue, tilt the head back, push the lower jaw forward;
- perform artificial respiration (mouth to mouth, mouth to nose);
- make an indirect heart massage (compression depth of at least 3 cm, at least 15 compressions for 2 breaths, the number of breaths - up to 16 per minute, the number of compressions - up to 70 per minute).
Loss of consciousness
If a person is breathing, but has lost consciousness, the algorithm of actions will be as follows:
- put the person on a flat hard surface;
- clear the airways;
- raise the legs up to provide blood access to the head;
- provide strong external stimuli (patting on the cheeks, splashing with water, giving a sniff of ammonia, vinegar).
Bruises, dislocations, fractures
 A bruise is the easiest injury that can be sustained in an accident. It is characterized by damage to soft tissues, accompanied by severe pain, difficulty in movement, and internal organs can be damaged. A tight bandage is applied to the site of the bruise, the damaged part of the body should be raised, cold is applied to the site of the bruise, and the person is provided with peace.
A bruise is the easiest injury that can be sustained in an accident. It is characterized by damage to soft tissues, accompanied by severe pain, difficulty in movement, and internal organs can be damaged. A tight bandage is applied to the site of the bruise, the damaged part of the body should be raised, cold is applied to the site of the bruise, and the person is provided with peace.
If after an accident the head hurts, feels sick, there is vomiting, then we are probably talking about a concussion. First of all, a person needs to ensure peace, put a cold on his head.
In the event of a fracture, the procedure for the rescuer is as follows:
- the mobility of the limb is excluded (special tires are superimposed, which can be replaced by any means at hand);
- with a fracture of the skull, a person is placed belly down;
- in case of a fracture of the jaw, the head is laid on its side, the lower jaw is fixed with a sling-like bandage;
- in case of a fracture of the clavicle, the hand is suspended on a scarf;
- in case of a fracture of the ribs, a bandage bandage is applied to the chest;
- in case of a pelvic fracture, plywood or any other hard material is applied to the back;
- in case of a fracture of the human spine, they are laid with their stomach down;
- in case of a fracture of the neck, a person is laid with his back down.
If a dislocation occurs during an accident, swelling, severe pain appear at the site of injury, the joint changes its position. Cold is applied to the injury site, an anesthetic is given. The limb is fixed until the doctor arrives.
Bleeding
In case of bleeding, it is important to stop it immediately, for this:
- if there is little blood, we wash the wound with a colorless liquid;
- if there is a lot of blood, we apply a tight bandage (if the bandage is soaked with blood, we still do not remove it);
- if there is a lot of blood, it flows like a fountain (arterial bleeding) - we clamp the artery with a tourniquet (lower part of the shoulder, upper part of the thigh).
The tourniquet is applied above the wound to the clothing. A tourniquet is applied quickly, removed slowly. The maximum time that a tourniquet can be on the body is 1 hour.
burns
If a person was burned during an accident, first aid is provided as follows:
- the lesion factor is eliminated;
- a burn of 1 and 2 degrees is cooled with clean water (flowing);
- a 3rd and 4th degree burn is cooled with a wet bandage.
The extent of the burn can be determined by outward signs. With burns of the 1st degree, redness appears, with 2nd degree - blisters, 3rd degree - bursting blisters, 4th degree - charring occurs, the skin loses sensitivity.
Burns prohibited.:
- lubricate the newly burned area with oil, creams, ointments;
- try to tear off stuck clothes;
- burst bubbles;
- urinate on the burn.
Transporting the victim to the hospital
 If it is not possible to call an ambulance or wait for the arrival of doctors, then the victim can be transported independently. The position of the patient depends on the nature of the injuries and the degree of damage.
If it is not possible to call an ambulance or wait for the arrival of doctors, then the victim can be transported independently. The position of the patient depends on the nature of the injuries and the degree of damage.
If there is damage to the head or spine, then the person is transported in the supine position. A person is transported on his stomach if he is unconscious or there are injuries to the abdominal cavity, while the lower limbs must be raised. If a person is unconscious and vomiting is present, then he should be laid on his side. The stretcher can be made independently from branches, tarpaulin and other improvised materials.
Regardless of whether a person is a driver or a passenger, knowledge of the rules for providing medical care is mandatory for everyone. Just a few minutes of the right action can save a person's life.
First aid to victims of a road traffic accident (RTA) is not always medical. It is important for a simple layman without a medical education to remember that in a critical situation, any action is better than inaction. The timely call of rescuers and doctors is already half the battle. But everyone needs to know the basics of first aid. Correct and balanced actions can save more than one human life.
ON A NOTE! For failure to provide assistance to the victims and leaving them in danger, penalties from a fine (up to 80,000 rubles) to 1 year in prison are provided (Article 125 of the current edition of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation dated 13.06.1996 No. 63-FZ).
First Aid Rules
The task of first aid is to eliminate the threat to the life of the victim. Fear of harm or disgust is inappropriate here, since first aid is not a medical category. The main thing here is to act coolly and without delay.
First of all you need:
1. Put up an emergency stop sign. At a distance of at least 15 meters from the vehicle in built-up areas and 30 meters outside built-up areas. If possible, turn on the emergency light signaling, in accordance with clause 2.5 of the Rules of the Road (SDA RF). This will save the victim and ourselves, while we help him.
2. Inspect the accident site and quickly assess possible threats.
Is it possible that
- a fire or explosion occurs;
- the car will roll down;
- broken high-voltage wires will fall on the machine.
If there is a threat to life, do not come close so that the rescuers who arrive instead of one victim do not find several.
If gasoline is spilled, be sure to disconnect the battery of the damaged vehicle.
3. Call for help by calling the Ministry of Emergency Situations - 112.
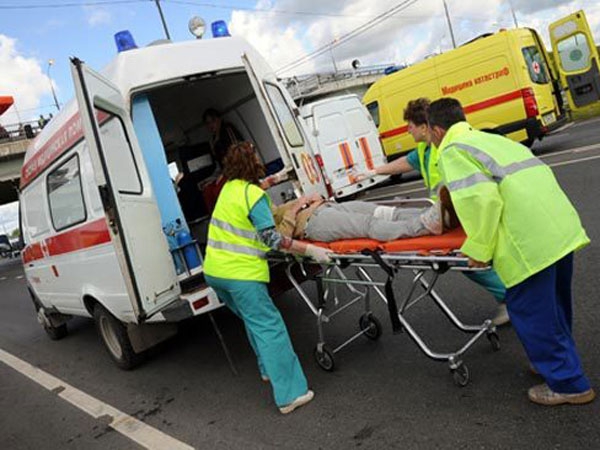 The more information the dispatcher collects about the incident, the sooner and more fully assistance will be provided. Therefore, when calling, you must quickly and clearly name:
The more information the dispatcher collects about the incident, the sooner and more fully assistance will be provided. Therefore, when calling, you must quickly and clearly name:
- what happened (car collision, pedestrian hit, etc.);
- road accident address or landmark (in which direction, on which highway, approximately how many kilometers);
- how many victims (to send the required number of ambulance teams);
- their gender and age (if we do not know how many, we say approximately: child, young, elderly, middle-aged);
- condition of the victims (unconscious, bleeding, trapped in a damaged vehicle, etc.);
- identify yourself and leave your phone number (the rescuers may need to clarify something).
IMPORTANT! If only one person provides assistance at the scene of an accident, and among the victims there is a child in a state of clinical death (without a pulse and heartbeat), then, having marked the scene with an emergency stop sign, you must immediately begin resuscitation. You can be distracted by calling an ambulance only after performing at least five cycles of pressure and artificial respiration (about 2 minutes).
4. Examine the victim, freeing access to him(open the door, break the window if necessary, etc.).
- If a person is conscious, establish and maintain constant contact with him. The main thing is to calm the victim. To say that he is not alone, they will not leave him. Then he himself will begin to help the rescuers: he will explain what and where it hurts.
- If a person is in shock, you need to calm him down so that he does not inflict additional injuries on himself in a panic.
- If unconscious, we check the pulse (on large arteries, with several fingers at once, so as not to miss a weak beat) and breathing.
- Whether there is bleeding and / or unnatural position of the limbs.
5. Provide assistance based on the results of the inspection, without removing from the car.
If there is no immediate threat to life, the victim does not need to be removed from the car.
If there is a threat to life (burning car, no pulse), we remove it to a safe place, if necessary, having previously fixed the neck with a Chance collar or improvised means.
Since one of the most common injuries to the driver and passengers in an accident is head and neck injuries.
IMPORTANT! If the airbag does not open, while assisting the victim, we try not to get between him and the steering (if the airbag opens, it injures both the victim and the person providing assistance). 5.1. If the victim is unconscious, we try to bring him to his senses.
5.2. If there is no pulse - an indirect heart massage (if there is a heartbeat, a heart massage cannot be performed).
5.3. If there is no breathing - artificial respiration.
Often you have to combine heart massage and artificial respiration:
- It is necessary to lay the victim on the ground. Tilt his head back (roller under his neck), insert a mouth-to-mouth artificial respiration barrier tube (if not, through a handkerchief or napkin), pinch his nose and, holding the patient's jaw, take 2 breaths into the victim's mouth.
- Place crossed palms just above the solar plexus. Perpendicularly with straight arms, make a sharp pressure so that the chest drops by 3-4 cm and let it rise. For two breaths - 15-30 clicks (compressions).
- With peripheral vision, you need to monitor whether the chest rises. If you breathe on your own, gently lay it on its side.
 5.4. We stop bleeding with improvised means.
5.4. We stop bleeding with improvised means.
In most cases, it is enough to put a sterile napkin on the wound and bandage it.
If the artery is damaged, and the blood gushes out in a wide pulsating stream, a tourniquet (for the limbs) will be needed.
- The tourniquet must not be applied to a naked body (it must be on a shirt, etc.).
- Slightly stretch the tourniquet and applying it 3-4 cm above the damage, the first round stops the bleeding.
Next, we put 3-4 more rounds side by side, and not on the first round, so that the area of squeezing is larger. - We attach a note - at what time the tourniquet was applied, since it is impossible to keep it for more than 1 hour so that the necrosis of the tissues that are located below the wound does not begin.
- If there are still no rescuers, after an hour, slowly release the tourniquet from the limb for 2-5 minutes, and then apply it again. And repeat this procedure every 15-20 minutes, each time fixing the new time of its application.
- The tourniquet must not be loosened if it is applied to stop bleeding in a limb amputated in an accident. Then it must be applied 5 cm above the injury site.
5.5. Fractures and dislocations are determined by the unnatural position of the body. The main help is in immobilization using splints or improvised means. Tires should capture the fracture site and 2-3 nearby joints.
5.6. Burns. In case of extensive burns, lay the victim up with the wound up, cover the burn with a clean cloth, put cold on top of the cloth, give an anesthetic and drink plenty of fluids. For burns of 1-2 degrees, the burn site must first be cooled with cold water.
Video: EMERCOM employees talk about first aid in case of an accident in the Fellow Traveler program
First aid kit motorist
Approved by Appendix No. 1 to the order of the Ministry of Health and Medical Industry of Russia of August 20, 1996 N 325 (as amended). In addition to dressings, the first aid kit includes gloves; device for artificial respiration "Mouth-Device-Mouth" and recommendations for the use of the first aid kit (Appendix No. 2). It is useful to supplement its composition with a disposable cervical collar and splints (usually made of cardboard). Other components (drugs, etc.) will only come in handy if you know how to use them correctly.
Even if you are an experienced driver with many years of experience or plan to limit your assistance in such a situation to just a timely call for an ambulance (which, in fact, is half of the whole thing), read the section ““, published on the official website of the Rules of the Road of the Russian Federation. Who knows, maybe it will help you save a human life.
Which do not always do without victims. As practice shows, hundreds of thousands of people die every year as a result of accidents, and not only those who are guilty of the accident, but also, by an unfortunate coincidence, simply found themselves in the center of events. Only 20% of road accident victims die on the spot. traffic accident due to injuries that were incompatible with life. Most often, people injured in a road traffic accident die because they were not provided with assistance in a timely manner. If the participants in the movement who happened to be nearby had not been inactive and had correctly carried out all the necessary medical manipulations, many could have survived. In addition to traffic rules, each participant in the movement, regardless of who he is (driver or pedestrian), must know how first aid is provided in case of an accident.
Every road user must be able to provide first aid
If a collision occurs on the road in which people were injured, then nearby drivers and passers-by should immediately come to the aid of the victims of the accident. However, the types of assistance provided are different, some participants in such an accident may be directly in the vehicle, others - lie on the road. For each of them, an individual approach should be sought, applying a certain algorithm for performing actions.
First aid for an injured pedestrian
As a rule, pedestrians often suffer as a result of an accident, and the driver of the car is far from always guilty of the incident, often, neglecting the rules and footpaths, “in a hurry” run out onto the road in an unspecified place, literally “jumping” under the wheels of a speeding car . Due to the collision of a pedestrian and a car, the first participant in the accident most often receives several different injuries at once. During the impact, the greatest force is exerted on the hip of the pedestrian, who, after an unexpected shock, rolls over and falls onto the road surface, additionally receiving blows in the head and neck. These injuries are most often received by people, so if this happens, eyewitnesses need to:
- call the emergency room or ask other people around to do it;
- to protect the place of collision, excluding the possibility of passage of other cars;
- in an unconscious person, you should feel the pulse and check for breathing. If neither pulse nor breathing is detected, then it is necessary to immediately turn him on his back and do an indirect heart massage, artificially supplying the lungs with oxygen (there is no need to wait for the arrival of doctors, since emergency measures can be effective only in the first 30 minutes);
- if a normal pulse and breathing are detected, then the injured pedestrian cannot be turned over, it is better to wait for the ambulance. The only exception is the situation when there is severe bleeding or vomiting. Immediate stop of bleeding should be carried out by any improvised means. When vomiting, it should be excluded from getting into the respiratory tract, for this, the person who has an accident is laid on his side.

First aid in case of an accident should not harm the injured pedestrian, which is why you should not disturb the injured person during the accident without unnecessary need. If caregivers do not have specialized devices and rigid fixators, then already broken vertebrae can be even more displaced, which in the future will result in severe complications and increased traumatic shock. If the accident occurred in spring or winter, when the road surface is cold enough, the victim must be covered with something additional to avoid hypothermia.
First aid for an injured driver or car passengers
In order for the provision of assistance in case of an accident to have a positive effect, it is necessary to take into account the nature of the injuries received by people in the vehicle. In the vast majority of cases, the driver and passenger in the front seat hit their heads hard during a collision. The contact of an important part of the body occurs directly with the steering wheel and dashboard. In such a situation, the victims are "rewarded" with injuries to the cervical vertebrae and head, often getting a concussion.
The second most common injury is considered to be a fracture of the ribs, because of it the lungs suffer greatly, ruptures of internal organs occur, supplemented by bleeding and all kinds of open fractures.
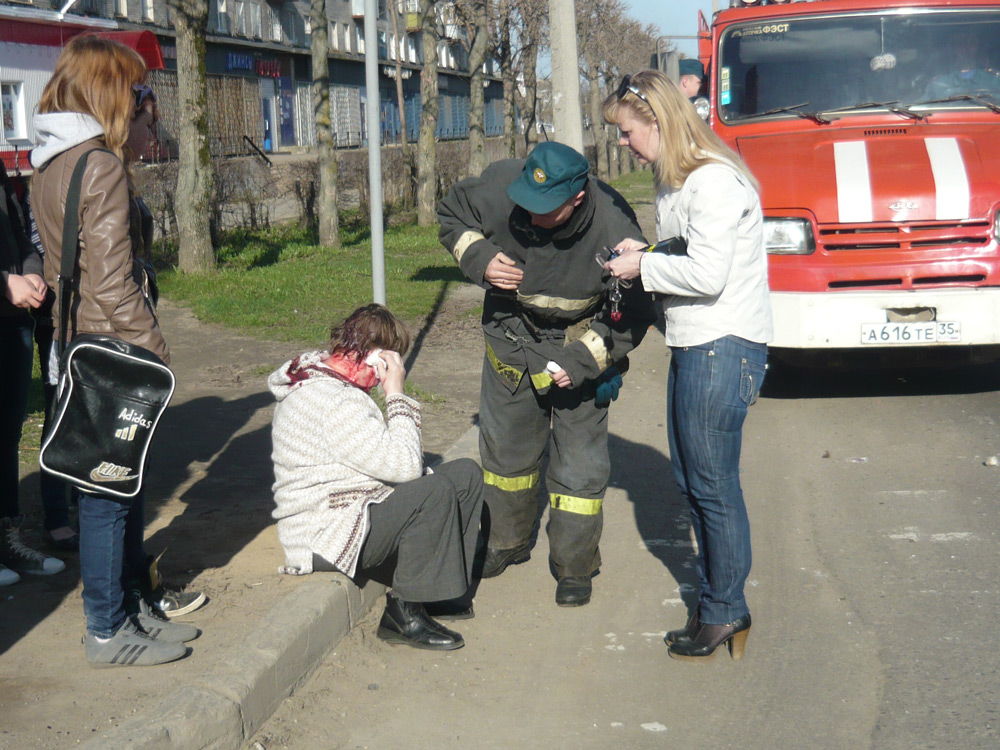

First aid in case of an accident is provided before the arrival of paramedics and other emergency services, only if there is a possibility of fire motor vehicle, passenger or driver has no pulse, anyone is bleeding heavily and cannot be stopped without first moving. If there is no obvious threat to the life of the injured, then it is highly undesirable to get them out of the car.
After the witnesses who came to the rescue decided to provide assistance, it is necessary, first of all, to determine the nature of the injuries received, among which may be:
- stop breathing and heartbeat;
- various types of bleeding;
- dangerous damage to the skull;
- all kinds of spinal injuries.
Assistance in case of an accident should be carried out, first of all, to those who are most injured. Only after that you should help the rest, who received simpler and lighter injuries. Observing this important rule, you can save all the participants in the accident and at the same time not get confused, scattering attention at once on everyone.
First steps
In order to properly provide timely assistance to victims of an accident, one should first assess the situation, sometimes a damaged vehicle poses a great danger to both passengers and those who are trying to save them. A broken car can explode very quickly, which is why everyone needs to be at some distance from a dangerous device.
If medical care is already being provided for victims of an accident, other bystanders should be aware that the section of the roadway on which the accident occurred must be fenced off with special signs or any suitable means.
If any of the victims of an accident has a temporary stoppage of the heartbeat, a set of resuscitation measures should be immediately carried out. The injured person needs to do an indirect heart massage with artificial ventilation of the lungs as soon as possible (according to the rules, the ratio of breaths and pressures is 1:15, in particular, there should be 15 compressions on the lower third of the chest for each breath). Medical assistance in case of an accident, which consists in carrying out such actions, should be carried out until the cardiac activity resumes.
Providing first aid to victims of an accident may consist in the need to stop severe bleeding, for which a tourniquet should be used. More minor cuts and injuries can be covered with simple dry clothing torn into bandages. Fractures should be immobilized. Carrying out any manipulation on the victim, one must not be silent, but constantly talk so that the latter does not have a clouding of consciousness.
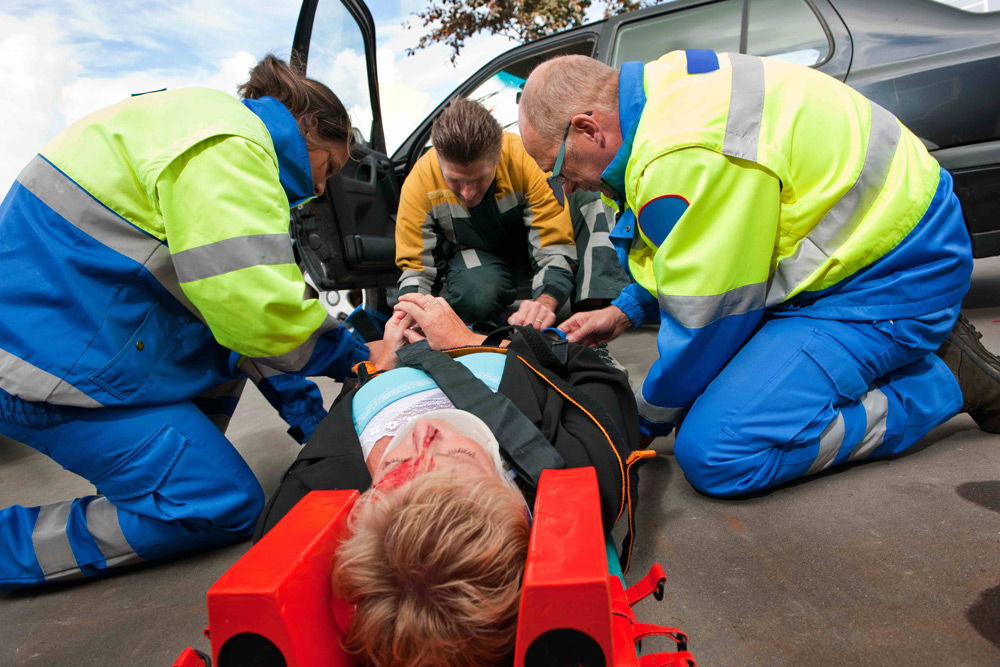

Carrying out urgent measures for the provision of first aid, one should be guided by one important rule: Do not further harm the injured person.
No matter how good the intentions of helping injured people are, you should not forget about safety, since a vehicle equipped with gasoline power unit, can burn out in just 5 minutes, in addition, the risk of an explosion must not be ruled out. All these circumstances must be taken into account, the actions of the first aid provider must be thought out in advance.
Medical assistance in case of an accident should be as accurate and balanced as possible. If it is impossible to do without the evacuation of a passenger in an accident, it should be borne in mind that his cervical spine may be damaged. Since many people face this injury, it should be taken into account that improper removal of the injured will inevitably lead to his death.
It will not be superfluous to determine the level of consciousness, for which you need to talk with the injured person, while fixing his head if possible. After applying the cervical collar, you can check the reaction of the eye pupil to light.
First aid for victims depends on the type of injury received.
clinical death
Medical assistance in case of an accident should be provided to all victims. Before performing any manipulations, you should know the nature of the damage.
Clinical death, for example, has several characteristic features: the victim has no consciousness, no breathing, no heartbeat. Moreover, with all of the above, the pupil is much larger than usual.
In order to properly provide first aid, it is critical to lay the person on their back, preferably on a hard and flat surface. Check the condition of the upper respiratory tract, if necessary, remove the retraction of the tongue or other foreign body. In this situation, it is important to monitor the position of the head, as it must be positioned behind, the chin in front, and the lower jaw slightly extended.
Medical care in case of an accident consists of several stages, for example, in case of weak or absent breathing, it is necessary to ventilate the lungs, in case of not detecting a heartbeat, an indirect heart massage.
During any resuscitation, it is important to regularly pay attention to the injured person, or rather to the reaction of his body (shrinkage of the pupil to which the light is directed, the appearance of a pulse and spontaneous breathing). Any of these signs is direct evidence of effective resuscitation.
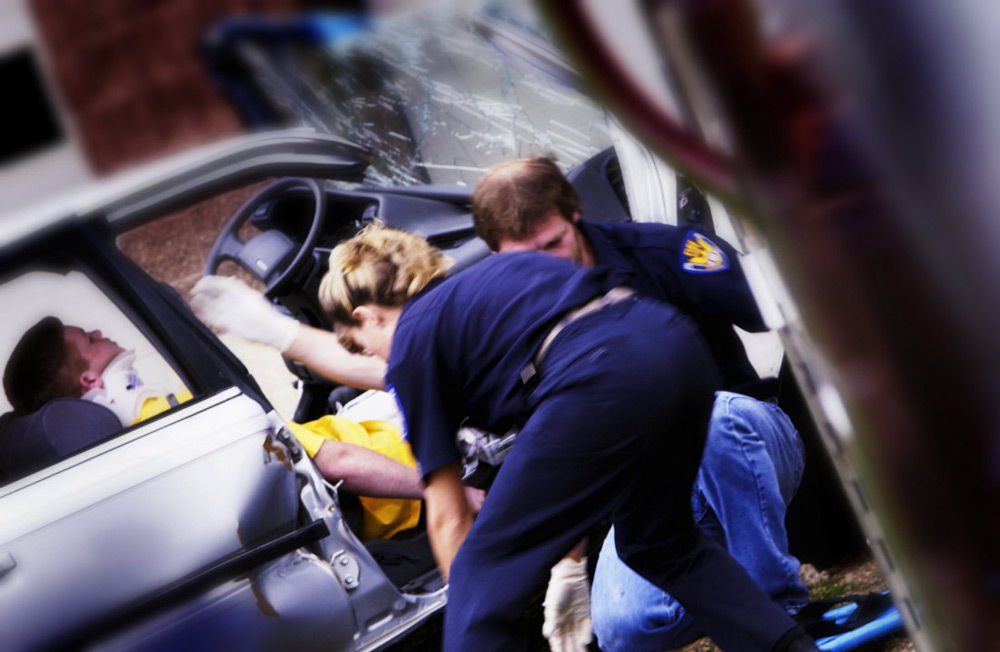

If there is normal breathing and heartbeat, then the first aid in case of an accident to an unconscious victim will be to evacuate him from the vehicle as a whole, in other words, you can get a person out of the car only if the cervical spine is fixed. After that, the victim should be laid on his stomach, and those who provide assistance are required to monitor the airway, monitor breathing and heartbeat. If necessary, it is necessary to carry out all kinds of resuscitation measures before the arrival of the ambulance team in order to save the life of the victim.
Bleeding
Anyone who has bleeding that is, in fact, a manifestation of some kind of injury needs medical attention after an accident. This type of disease can be internal or external. If the first type occurs, the injured person is likely to have too pale skin, the body will break through cold sweat, and increasing weakness and loss of consciousness are not ruled out. In this situation, you need to immediately, but very carefully, put the victim on his back and slightly raise his legs.
With external bleeding, its type should be determined, since venous loss is accompanied by the release of dark blood in a plentiful stream, so the wound should be bandaged with a tight bandage
In case of arterial blood loss, it is important for the helper not to hesitate, as bright scarlet blood comes out in a powerful pulsating stream. To prevent this, you should pinch the injured vessel with your fingers a little higher than the place where the open wound is located. In the future, it is important to apply a tight bandage.
Capillary blood loss is typical for those who have severely damaged a large area of skin. With this injury, the entire outer surface of the wound bleeds. You can help the injured by means of a hemostatic sponge and the imposition of a tight bandage.
fractures
First aid in case of an accident should be timely, if the injured person has a suspicion of fractures, you should try to understand what type of fracture this person has: open or closed.
Closed bone injury is characterized by the presence of severe pain, increased pain during movement, as well as external deformation and swelling.
At open damage there is also deformation and swelling of the injured part of the limb, however, in addition, the patient must have a wound, from which fragments of bone substance can protrude.
Before the arrival of the ambulance team, you need to try to anesthetize the wound, disinfect it, put a splint on it, while making the joint immovable both above and slightly below the damaged area. Only in no case should you try to set damaged bones on your own, this should only be done by professionals.

burns
Providing first aid to victims of an accident should be carried out not only quickly, but also thoughtfully so as not to cause even more harm to the injured. If a person who has had an accident has multiple burns on his body, he needs to be helped, having previously determined the degree of injury.
Redness of the area of the skin with a small number of blisters is a manifestation of a burn of the 1st or 2nd degree. More severe 3rd and 4th degree burns are characterized by charred skin and strong discharge of a mixture of blood and fluid.
More simple injuries should be tried to substitute under cold water, then bandaged with a clean cloth and put cold on top.
Serious burns of the 3rd and 4th degree should be immediately covered with sterile rags, on top of which place cold.
If a large part of the body is covered with burns, the injured person should be placed so that the maximum number of wounds is located on top, then all damaged areas should be covered with a clean cloth, cold should be applied, anesthetized and the patient should be drunk.
First steps if a foreign body is found in the upper respiratory tract
Effective first aid in case of an accident for a patient who has a foreign object in the upper respiratory tract can only be in the first 3-5 minutes. If the victim begins to cough sharply, he is worried about choking with vomiting, profuse lacrimation, a complex of resuscitation measures should be immediately applied.
First of all, you can try to get the object through blows applied with an open palm to the interscapular region of the patient. If these manipulations did not bring a positive effect, you need to stand behind the person, grab him and press the epigastric region with your hands folded into the lock.
An unconscious person can be helped by turning him on his back, then with his hands, taking out an object, sharply press on the epigastric region.
Actions in case of loss of consciousness
The first medical, if it is provided to an unconscious person, should depend on the location of the victim. Most often, people lose consciousness who are in the scorching sun for a long time, experience a lack of air or severe emotional stress. In addition, loss of consciousness may accompany internal bleeding or any cardiovascular disease that is in a progressive phase.
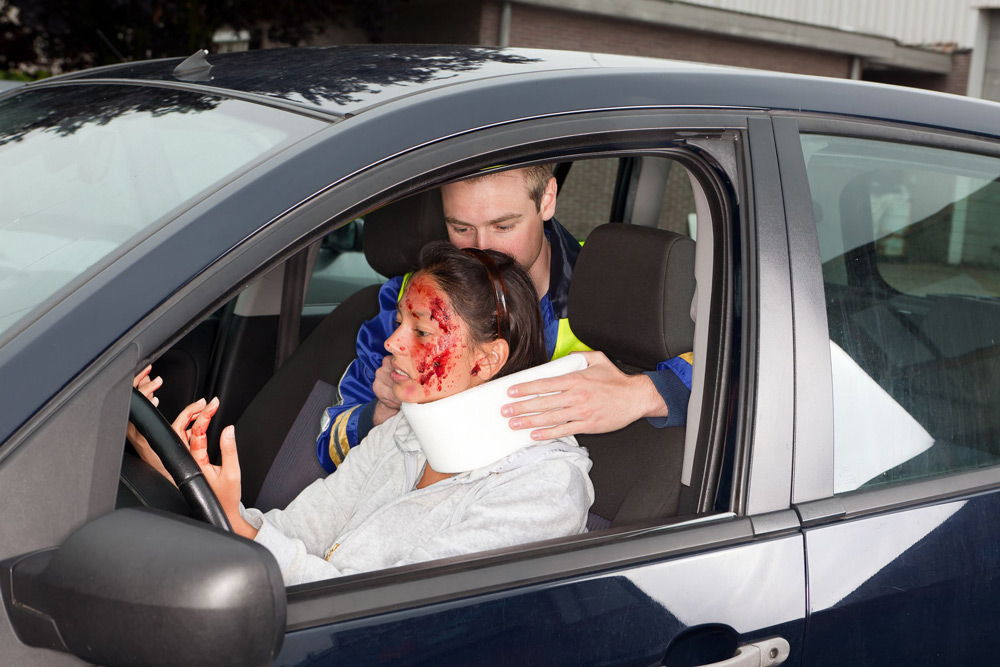

The first action in the absence of consciousness, breathing or heartbeat should be resuscitation.
In the case when the heartbeat and breathing are normal, and consciousness is absent for less than two minutes, the victim should be laid on his back, while slightly raising his legs, freeing his neck from a tight collar or tie, try to provide the maximum flow of fresh air. You can bring ammonia to your nose, lubricate the area of \u200b\u200bthe temples with a moistened swab.
If a person does not regain consciousness for more than three minutes, he should be placed on his stomach, checked and, if necessary, freed the upper respiratory tract, then put something cold on his head. All the time before the arrival of the ambulance team, you need to check your breathing and heartbeat.
seizure
A person who has a seizure should be given first aid immediately. The cause of this condition may be epilepsy or hysteria. The patient, unexpectedly for others, may faint, a second before which a scream, convulsions and foam from the mouth may appear. The victim is likely to have dilated pupils, maintain their pulse, and relax their pelvic muscles, which may result in involuntary urination.
First aid for an accident with a seizure is to position the victim on his side, lower his shoulders to the floor and insert a thick tissue roller into his teeth.
A person in a seizure during a convulsion or a fall can severely injure his head, people nearby should try to ensure his safety.
Chest pain
If a person suffers from a cardiovascular disease, at the time of an accident, his state of health may deteriorate greatly. The victim will be disturbed by pressing, burning or cutting pains felt in the central part of the sternum or the left side of the chest. In addition, the patient may experience weakness, cold sweat pierces him.
Assistance in case of an accident consists in providing rest to the patient, providing fresh air flows. There will be no extra nitroglycerin capsule, which should be put under the tongue. If the pain does not disappear after 20 minutes, you need to re-supply the victim with nitroglycerin.
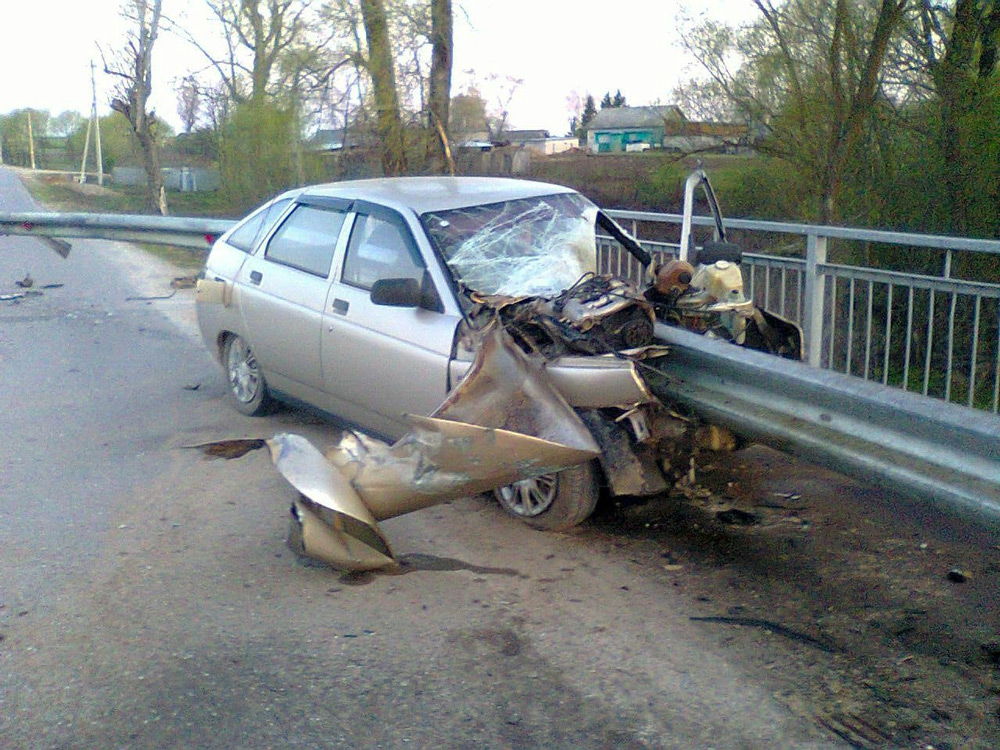

Allergic reaction
Sometimes rendering assistance in case of an accident, even in the case of correctly performed manipulations, can worsen the condition of the victim. Due to the sensitivity of the body to any drug or painkiller, a small punctate rash may appear on the patient's skin, accompanied by itching and increasing swelling of the eyelids and lips.
The resulting allergic reaction can be minimized by applying cold to the area of the body where the injection was made. After that, the patient can be given 2 tablets of Tavegil. In any case, using any medications, you should carefully read the instructions in order to know the dosage.
Conclusion
Medical assistance in case of an accident can be provided to the victim not only by random passers-by, who at that moment, by coincidence, was nearby, but also directly by the patient himself. If the condition of the injured person is not aggravated by severe injuries, bruises, cuts, blood loss and loss of consciousness, you should try to provide first aid to yourself and the other participants in the accident. In such a situation, one should not hesitate and doubt, one should act promptly, clearly and deliberately.
The best prices and conditions for the purchase of new cars
Credit 4.5% / Installment / Trade-in / 95% approval / Gifts in the salonMas Motors
created: Tue, 10/07/2012 - 14:56
updated: Thu, 01/06/2017 - 11:33
The main causes of death in road accidents:
Injuries not compatible with life - 20%
- ambulance delay - 10%
- incorrectly rendered first aid or inaction of eyewitnesses - 70%.
Why is this happening, how to help a person injured in an accident? After all, in a driving school, everyone learns the rules for providing first aid in case of an accident. But for some reason, the majority remains either indifferent to someone else's grief, or do not know how to help. We urge all motorists not to remain indifferent and to familiarize themselves (or repeat) with the basic principles of first aid in case of an accident.
Accidents often happen in areas far from hospitals. This is one of the main reasons why an ambulance cannot quickly get to the scene of an accident. And this pre-hospital period is in our hands. The ability to provide assistance at this stage is greatly appreciated.
Ensuring safety at the scene of an accident.
1. Turning on the emergency light signaling and setting the emergency stop sign.
2. Assessment of the situation and confidence in one's own safety, otherwise the number of victims may increase. A car with a gasoline engine burns out in 5-7 minutes, there is a possibility of an explosion. Therefore, it is necessary to turn off the engine, disconnect the battery (disconnect the wires from the battery with all possible ways tear, cut, unscrew). If the car crashed into a pole with power lines, then a break in the lines is possible. You have to be careful.
3. Call an ambulance and rescue services. Let always in your phone book be memorized the numbers of rescue services:
"03" in Russia - ambulance service
"01" in Russia is the fire department, but through it you can always call an ambulance and rescue service
The sequence of assistance in case of an accident.
1. We call an ambulance.
2. It is necessary to remove the victim from the car. This is a very crucial moment, since it is possible to aggravate the severity of the injuries. The main injuries in road accidents are traumatic brain injury, injuries of the thoracic region and lower extremities. Before removing the victim from the car, it is necessary to eliminate everything that could interfere with this. The person is pulled out, taking him by the armpits.
Since in an accident a person receives various kinds of injuries, bruises, fractures, no sudden movements can be created. In no case should you pull and stretch the limbs. And also in no case do not bend the limbs and torso. If there is a suspicion of a fracture of the spine, then such a patient is placed on the stomach so that the fracture site remains relatively calm.
3. After removing the victim, everything must be done as carefully as possible and assess his condition as quickly as possible. First you need to remove the squeezing clothes to ensure the flow of oxygen (remove the tie, tear the clothes, loosen the belt, etc.). Any careless movement or pressure can only increase the pain, be careful.
4. Assess the condition of the victim. First you need to assess the state of vital functions, the nature of first aid will depend on this:
Respiration: the normal number of breaths per minute in an adult is 16-20, in children - 20-23. The victim may develop both rapid breathing (25-30) and rare (8-10), which may indicate the development of shock;
- pulse: it is better to feel it on the carotid (neck) or radial artery (in the place where the watch is worn). Normally 60-80, in children 80-90. A fast pulse or slow (less than 60) or irregular pulse may be a sign of shock;
- pupillary reaction: in healthy people, the pupil constricts in the light and expands in the dark. If the victim's pupils are dilated and do not respond to light, this is a sign of a life-threatening condition.
- skin: normal pink color and warm to the touch. With fainting and blood loss, they become pale and cold. In case of severe respiratory failure and blood loss - cyanotic. Rescuers should have 5-10 seconds for such an assessment. Because every minute matters.
Resuscitation of the victim with signs of clinical death.
Each of the following signs is not the main and reliable sign of clinical death. The diagnosis is made when all or most of the following are present:
Lack of consciousness;
Lack of breathing;
Absence of pulsation on large vessels (carotid or femoral). It is better not to check the pulse on the radial artery, since with systolic pressure (upper) 50-60 mm Hg. he is already disappearing;
pupil dilation;
Changes in the color of the skin and mucous membranes (the appearance of pallor or more often severe cyanosis).
clinical death is the period between life and death, in which there are no clinical signs of life, but vital important processes still going on in the body. This is the period when you can save a person. When resuscitation is provided in the first 3 minutes, the probability of salvation is 75%, if the time is delayed up to 5 minutes, the probability of salvation is 25%. And if more than 10 minutes, then saving a person is already unrealistic. Because in a matter of minutes, the human brain dies.
General principles of resuscitation:
The victim must be placed on a hard surface;
A roller is placed under the neck to prevent the tongue from sinking;
Indirect cardiac massage with artificial respiration. The ratio of the number of chest compressions and artificial breaths - when assisted by one person for 2 breaths, 15 compressions, when assisted by two - for 1 breath, 5 compressions. The total number of breaths is 12-16 per minute, chest compressions are 60-70 per minute. Blowing air should take 1-2 seconds. The pushing of the chest should be 4-5 cm, in children 2-3 cm and is made with the base of the palm of one hand. Massage is continued until complete recovery of cardiac activity.
Signs of effective resuscitation:
The appearance of a pulsation in the carotid artery;
Constriction of the pupils;
The skin turns pink;
The appearance of spontaneous breathing.
General principles of first aid in case of an accident.
Stop bleeding;
In the absence of breathing, start artificial respiration;
In the absence of a pulse, along with artificial respiration, do an indirect heart massage;
Treat wounds, apply a bandage. In case of fractures, apply splints.
Car first aid kit.
Dressings were added to the new composition of car first-aid kits, since the previously included 3 bandages were not enough to help even one victim. The exclusion of drugs is due to the fact that in the heat the temperature can reach 40-50 degrees Celsius. This is a very gross violation. At high temperature drugs can change their properties and be life-threatening. Yes, and drugs such as analgin and activated charcoal have nothing to do with saving a person's life.
The composition of the car first aid kit is designed to provide first aid in case of severe injuries that can threaten a person's life. Further, the Law states: “At the same time, the driver may, at his discretion, store medicines and medical products for personal use in the first-aid kit, taken by him independently or recommended by the attending physician and freely available in pharmacies.” In addition to the composition of the first-aid kit, recommendations were developed for its use.
